College tuition costs have been steadily rising, making it challenging for many families to afford higher education. Fortunately, financial aid programs like the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) exist to help students pay for college through grants, scholarships, work-study, and student loans. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what FAFSA is, the types of financial aid it offers, eligibility requirements, and a step-by-step process to fill out the FAFSA form. So, let’s dive in and unlock the door to federal financial aid!
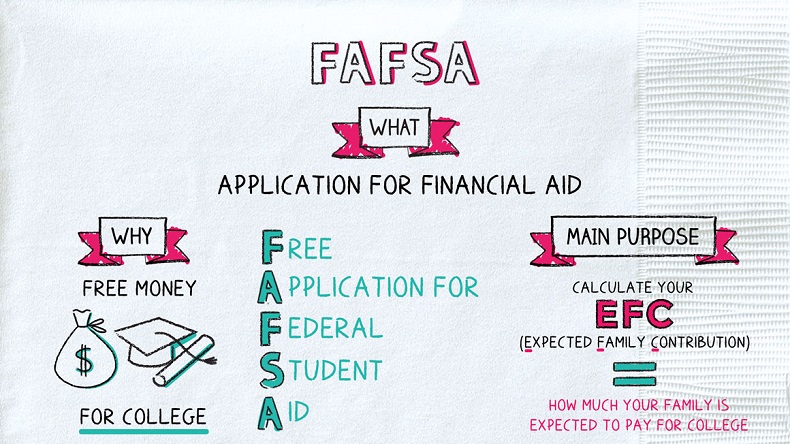
What is FAFSA?
FAFSA, short for the Free Application for Federal Student Aid, is a free form that serves as a gateway to federal financial aid programs. By completing the FAFSA, students can access grants, work-study opportunities, and student loans. Some states and colleges also rely on the FAFSA to determine eligibility for their financial aid programs. The form collects financial information to assess whether the applicant qualifies for need-based or non-need-based aid. It is essential to understand the FAFSA process and gather the necessary documents to ensure a smooth application experience.
Types of Financial Aid

Submitting the FAFSA opens doors to various types of financial aid. These include grants, work-study programs, and student loans:
Grants
Grants are a form of gift aid that does not require repayment and are typically awarded based on financial need. One well-known grant is the Pell Grant, available to undergraduate students. In the 2023-24 academic year, the Pell Grant awarded up to $7,395. Other grants may also be available through federal, state, or institutional programs.
Work-Study Programs
The work-study program provides part-time jobs for undergraduate and graduate students with financial need. These jobs are often available on-campus and may be related to the student’s field of study. However, competition for work-study positions can be high, and applicants must apply separately for these opportunities.
Student Loans
Federal student loans, such as Direct subsidized and unsubsidized loans (also known as Stafford loans), are accessible through the FAFSA. Unlike grants, student loans must be repaid with interest. It’s important to remember that accepting the full loan amount offered is not mandatory. Students should carefully consider their needs and only borrow what is necessary.
Additionally, some schools and private organizations review the FAFSA when considering students for scholarship awards, particularly those based on financial need.
Eligibility Requirements for Financial Aid
Contrary to popular belief, there are no income limits for the FAFSA. However, certain types of aid, like the Pell Grant and work-study programs, require demonstrating financial need. The main eligibility requirements for financial aid are as follows:
-
U.S. citizenship or eligible noncitizen status.
-
Possession of a valid Social Security number, with exceptions.
-
High school diploma, GED certificate, or alternative qualifying education.
-
Enrollment in or acceptance by an eligible degree or certificate program.
-
Enrollment in at least half-time attendance at a qualified educational institution.
-
Maintenance of satisfactory academic progress while in school.
How to Fill Out the FAFSA
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/quick-guide-how-fafsa-loans-work.aspfinal-095c438b775f49488e405992d7f8feba.jpg)
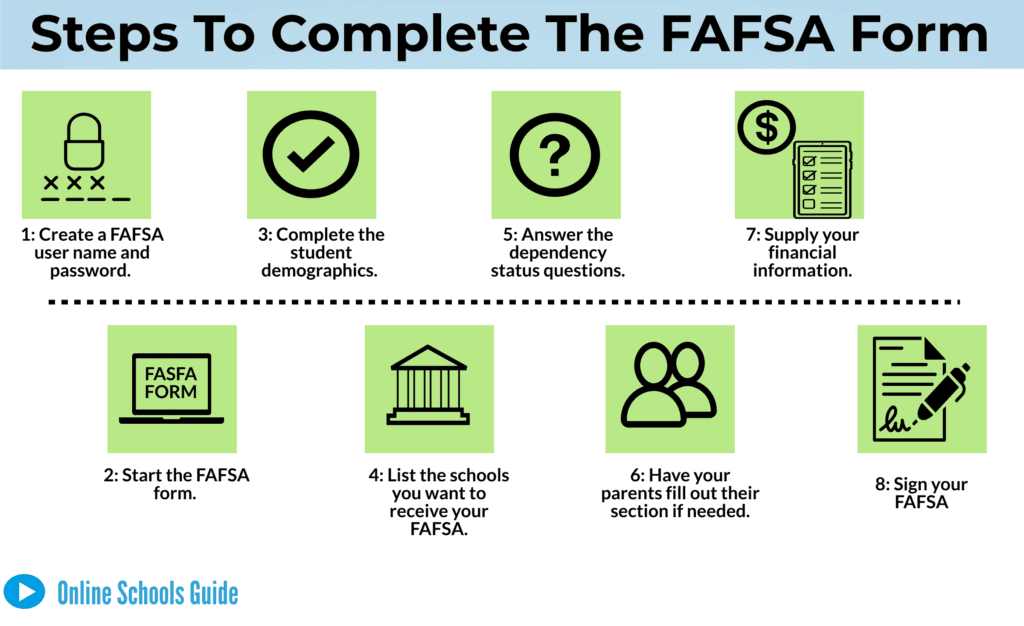
Filling out the FAFSA may feel intimidating, but with proper guidance, it becomes more manageable. Here is a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
Step 1: Create Your Federal Student Aid (FSA) ID
To begin, you need to create your Federal Student Aid (FSA) ID, which serves as your username and password for signing and submitting the FAFSA. If you are a dependent student, your parents will also need their own FSA IDs. A Social Security number is required to obtain an FSA ID. If your parents do not have a Social Security number, they can still sign and submit a FAFSA by printing and mailing the form.
Step 2: Gather Your Documents
Before starting the FAFSA, gather the necessary documents, including:
-
Social Security numbers for yourself and your parents (if applicable).
-
Driver’s license number (if applicable).
-
Alien Registration number (if you are not a U.S. citizen).
-
Federal tax information, including IRS tax returns.
-
Records of any untaxed income.
-
Information on cash, bank account balances, investments, real estate (excluding primary home), and business/farm assets.
Rest assured that the Federal Student Aid website protects your information through encryption. As long as you keep your FSA ID confidential, your personal data should remain secure.
Step 3: Indicate Your Dependency Status
The FAFSA includes a series of questions to determine whether you are a dependent or independent student. Most students under 24 years old are considered dependents, while those 24 or older are typically considered independents, with a few exceptions.
Step 4: Provide Financial Information
This step is where the FAFSA delves into financial details. Separate sections require information from both the student and, if applicable, their parents. It is crucial to ensure that the correct person’s information is entered in the appropriate section to avoid calculation errors and delays in financial aid awards. Labels at the top of each page indicate whether it is for the parent or student.
The income and asset-related questions may resemble those encountered in mortgage applications. Fortunately, the FAFSA offers a simplified option through the IRS Data Retrieval tool. Eligible applicants will find a “Link to IRS” button, allowing the automatic transfer of tax information from previous years.
Step 5: List Your Schools
You can list up to 10 schools on the FAFSA to receive your application information. It is mandatory to list at least one school. Each school has a unique federal code, which can be found using the Federal School Code Search tool. Schools rely on the FAFSA to determine financial aid offers.
Step 6: Sign and Submit the FAFSA
After answering all the questions and reviewing your information, you can sign and submit the FAFSA using your FSA ID. Dependent students will require their parents’ signatures as well.
Step 7: Review Your Student Aid Report (SAR)
Within three days to three weeks after submitting the FAFSA, you will receive a Student Aid Report (SAR). The SAR summarizes the information provided and should be reviewed for accuracy. If any mistakes are found, corrections can be made. Occasionally, the SAR may indicate that you have been selected for verification, which requires providing additional documentation to validate the information provided. This is a routine process, and being selected does not imply wrongdoing.
FAFSA Deadlines
Understanding FAFSA deadlines is crucial to ensure timely submission. There are three types of deadlines to consider:
-
Federal Deadline: The federal deadline is June 30, at the end of the applicable school year. However, submitting the FAFSA at this point would have little impact since the academic year would already be over.
-
State Deadline: Most states set earlier deadlines than the federal deadline, typically falling in January or February. It is essential to check your state’s FAFSA deadline on the StudentAid.gov website.
-
School Deadline: Individual schools also establish their own FAFSA deadlines. For example, Boston University has an early decision deadline of November 1 and a regular admission deadline of January 4. Check your school’s financial aid website for specific deadlines.
It’s worth noting that some colleges may require an additional form called the CSS Profile to determine eligibility for institutional aid. Unlike the FAFSA, the CSS Profile has a fee associated with it.
To maximize financial aid opportunities, it is highly recommended to submit the FAFSA as soon as possible. Many sources of financial aid operate on a first-come, first-served basis. Filing early increases the chances of qualifying for more grants compared to those who submit later.
Conclusion
Completing the FAFSA is a crucial step in unlocking federal financial aid for college. By understanding the process and gathering the necessary documentation, you can navigate the FAFSA application with confidence. Remember to submit the FAFSA as early as possible to maximize financial aid opportunities. By taking advantage of the grants, work-study programs, and student loans available through the FAFSA, you can make higher education more accessible and affordable.