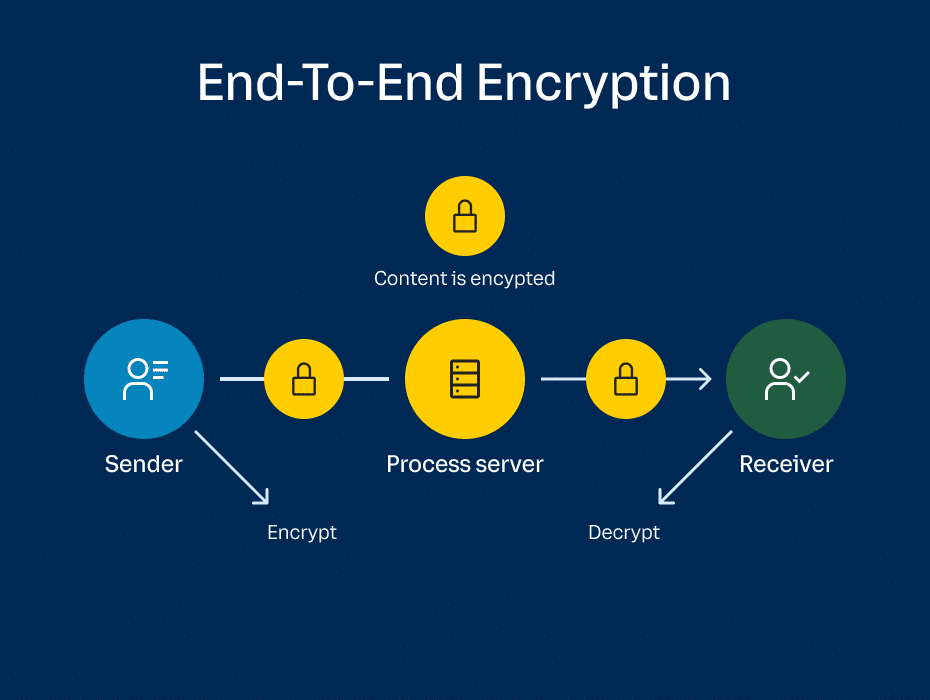
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a secure method of communication that ensures the privacy and confidentiality of your online conversations. This encryption technique protects your data by encrypting it at every stage of its journey from one device to another. In this article, we will explore what end-to-end encryption is, how it works, and its advantages over other types of encryption.
Understanding End-to-End Encryption
Encryption is the process of converting readable data, such as a plaintext email, into unreadable ciphertext using a cryptographic key. End-to-end encryption takes this concept a step further by encrypting your data at both the starting point (your device) and the final destination (the recipient’s device). This means that only the authorized parties involved in the communication can decrypt and access the data.
When you use end-to-end encryption to send an email, for example, the content of your message is inaccessible to third parties, including network administrators, internet service providers, hackers, and even the email service provider. The recipient holds the unique decryption key required to unlock and read the encrypted message.
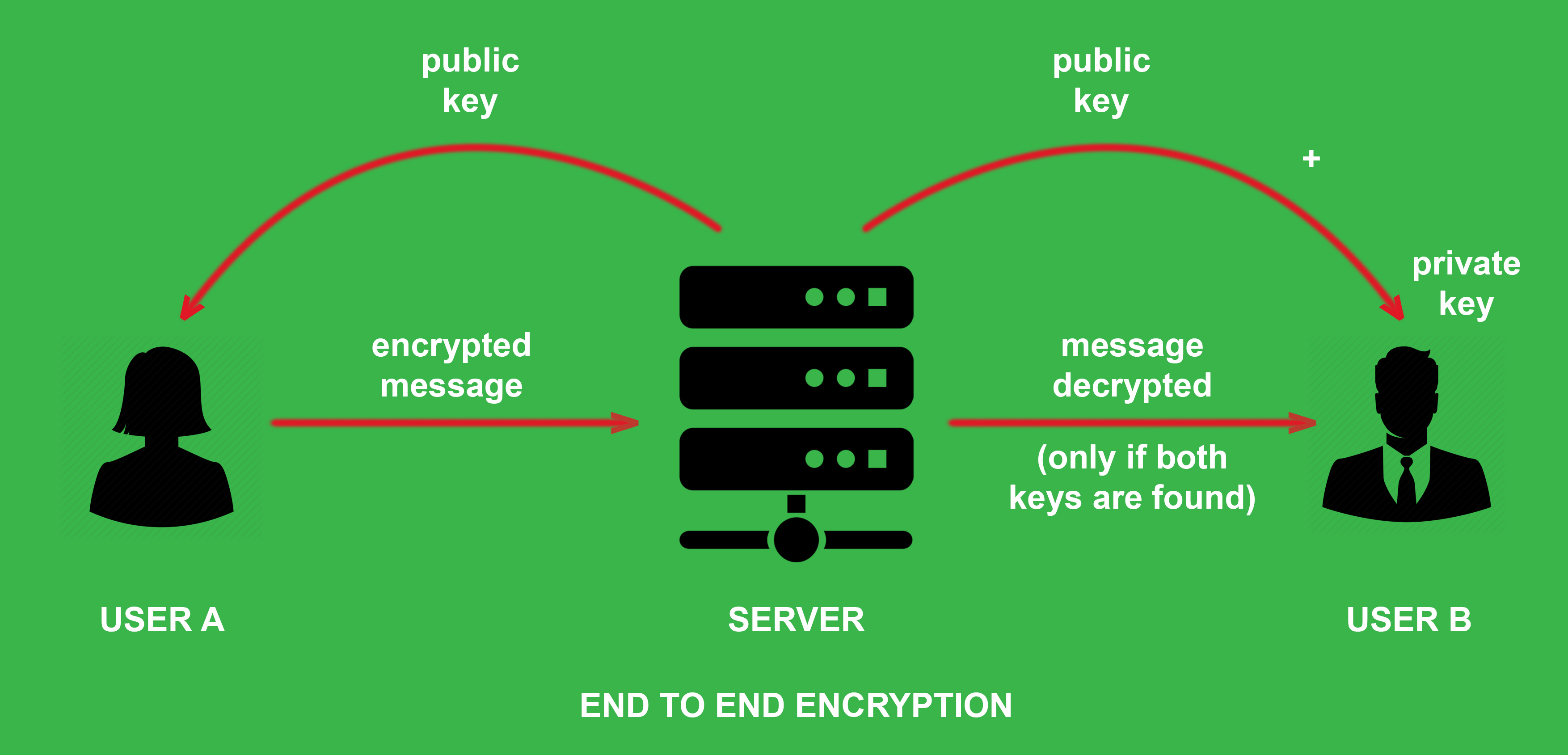
How End-to-End Encryption Works
To understand how end-to-end encryption works, let’s take a closer look at the process. Imagine Bob wants to send a private message to Alice. Alice has a public key and a private key, which are mathematically related cryptographic keys. Bob uses Alice’s public key to encrypt his message, transforming it into ciphertext.
During transmission, the encrypted message may pass through various servers, including those owned by email and internet service providers. Despite their attempts to intercept or read the message, it is computationally infeasible for them to convert the ciphertext back into readable plaintext. Only Alice, with access to her private key, can decrypt the message when it arrives on her device.
If Alice wants to reply to Bob’s message, she would encrypt her response using Bob’s public key, ensuring that only Bob can decrypt and read the message.
End-to-End Encryption vs. Other Security Paradigms
End-to-end encryption stands out from other security paradigms, such as point-to-point or in-transit encryption like the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. While TLS encrypts data between endpoints, it does not provide end-to-end encryption. Emails sent through standard email providers like Gmail or Hotmail are encrypted in transit using TLS, but the email service providers have access to the unencrypted content of the messages. In contrast, end-to-end encryption services like Proton Mail eliminate this possibility since the service provider does not possess the private key required for decryption.
By using end-to-end encryption, your data is protected from unauthorized access, reducing the risk of leaks or attacks. It ensures data integrity, preventing tampering or modification of the information during transmission. Additionally, end-to-end encryption keeps your data private, giving you control over who can access and read your emails. This level of privacy is crucial for individuals living under oppressive regimes, dissidents, activists, and journalists.
Advantages of End-to-End Encryption Services
End-to-end encryption offers several advantages over other security paradigms. Let’s explore some of the benefits:
1. Enhanced Data Security
End-to-end encryption significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Even if a hacker gains access to the servers where encrypted data is stored, they cannot decrypt the information without the private key.
2. Data Integrity
When properly implemented, end-to-end encryption ensures that the data remains intact and unaltered throughout its journey. This is particularly important when sharing sensitive information that must be delivered accurately.
3. Privacy and Confidentiality
End-to-end encryption prevents email service providers or any third party from accessing the content of your messages. Unlike standard email providers, E2EE services like Proton Mail do not have access to the private key required for decryption, ensuring your privacy and confidentiality.

4. Protection of Free Speech and Democracy
End-to-end encryption plays a crucial role in protecting free speech and democracy. By preventing governments from accessing citizens’ data, it safeguards individuals, activists, and journalists from potential persecution or intimidation.
How to Use End-to-End Encryption
Using end-to-end encryption is easier than ever, thanks to services like Proton Mail. When you use Proton Mail, your messages are automatically encrypted whenever a public key is available for the recipient. This means that when you send an email to someone who uses Proton Mail or PGP, the message is end-to-end encrypted without any additional steps required.
To start using end-to-end encryption, you can sign up for a free Proton Mail account. Proton Mail also offers an Easy Switch feature, allowing you to transfer your emails and calendars from less private providers quickly.
Frequently Asked Questions about End-to-End Encryption
What is ciphertext?
Ciphertext refers to encrypted data that is unreadable without the unique decryption key. Encryption algorithms scramble plaintext into ciphertext to protect the data from unauthorized access.
What is encrypted with end-to-end encryption?
When using end-to-end encryption with Proton Mail, the message body and attachments are fully encrypted whenever a public key is available for the recipient. If the recipient is not using Proton Mail or PGP, the message will only be end-to-end encrypted if you use the Password-protected Emails feature. Otherwise, the message will be encrypted in transit using TLS and will be readable by the recipient’s email provider.
What are encryption keys?
Encryption keys are random strings of bits used by encryption algorithms to encrypt and decrypt data. They are essential for converting plaintext into ciphertext and vice versa. In end-to-end encryption, both the sender and receiver have their own public and private keys.
What is PGP?
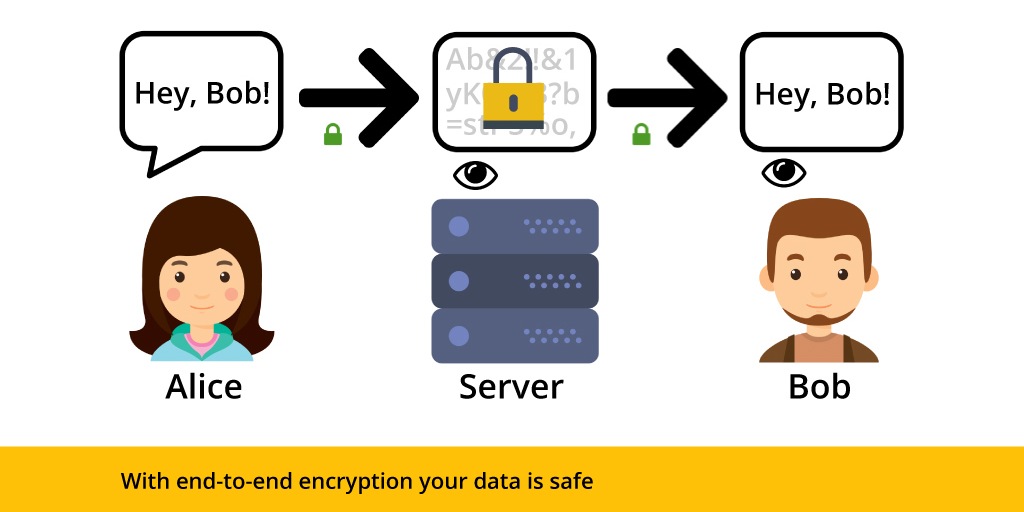
PGP, which stands for Pretty Good Privacy, is a widely used email encryption system. It transforms messages into ciphertext on the sender’s device, ensuring their privacy and authenticity. Proton Mail’s end-to-end encryption is based on an open-source version of PGP.
In conclusion, end-to-end encryption provides a secure and private means of communication by encrypting data at every stage of its journey. By understanding how it works and leveraging services like Proton Mail, you can protect your data from unauthorized access and maintain your privacy and confidentiality online. Embracing end-to-end encryption not only enhances data security but also upholds the principles of free speech and democracy in the digital age.