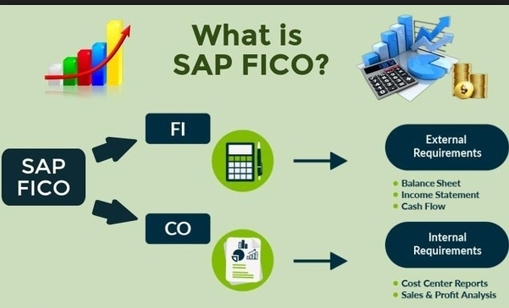
SAP FI, also known as SAP Finance, is a fundamental module of SAP ERP Financials that focuses on managing financial obligations within a business. It works in conjunction with SAP Controlling (CO), which handles cost control and is the other part of SAP Accounting. Together, SAP FI and SAP CO form a complete module commonly referred to as SAP FICO. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of SAP FI, its sub-modules, and the features that make it an essential tool for financial management within organizations. So, let’s get started!
What is SAP?
SAP is a German-based company that stands for Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing. It is a market leader in providing business solutions through software applications and services, catering to diverse industry needs. SAP offers a range of modules designed to address specific business requirements.
SAP ERP Financials

SAP ERP Financials is a powerful tool that enables organizations to enhance their financial performance by effectively managing liquidity, streamlining processes, and reducing costs. It encompasses various functionalities that provide comprehensive business support in critical areas such as finance and accounting, cost control, financial supply chain management, and treasury management.
SAP Financial Accounting (SAP FI)
SAP Financial Accounting, also known as SAP FI, facilitates company-wide control and integration of financial information, crucial for strategic decision-making. It adheres to international accounting standards like the US GAAP and TFRS, ensuring compliance with legal and accounting regulations in multiple countries.
Sub-Modules of SAP FI
SAP FI consists of several sub-modules that enhance its efficiency and user-friendliness. These sub-modules include:
-
New General Ledger (New G/L)
-
Accounts Payable (AP)
-
Accounts Receivable (AR)
-
Asset Accounting (AA)
-
Bank Accounting (BA)
-
Special Ledger (SL)
Let’s explore each sub-module in detail.
New General Ledger in SAP FI (New G/L)
The SAP New General Ledger revolutionizes financial accounting and reporting by eliminating the need for multiple ledgers. It offers comprehensive support for both financial and managerial accounting within a single application. The New G/L significantly improves financial accounting by enabling real-time, rules-based allocations between business units and automating the reconciliation of journal entries. This eliminates the necessity of reconciling multiple applications for enterprise-wide reporting requirements.
Features of New G/L in SAP FI
The New G/L in SAP FI introduces several features that enhance financial accounting and reporting:
-
Parallel Accounting: SAP New G/L allows the maintenance of multiple parallel ledgers to support diverse currencies and financial reporting standards such as IFRS and US GAAP. These parallel ledgers can be updated through a single posting transaction using defined business rules.
-
Document Splitting: The New G/L offers the option of document enhancement or online split, streamlining the process of posting transactions and allocating them to different cost or profit centers. Document splitting functionality can also be applied to customer-defined and industry-specific fields.
-
Single Reconciled Database: The New G/L features a single reconciled database with robust partitioning functionality. Multiple ledgers can be created within this database, including company-code segment and profit-center reporting dimensions, and custom fields.
-
Real-Time Reconciliation and Integration: Special ledger postings automatically roll up to the general ledger (G/L) through a common reconciled database, eliminating the need for manual or automated reconciliation. This ensures that managerial and financial accounting are always reconciled with the G/L.
-
Fast Close: The New G/L accelerates the period-end closing cycle by automating several period-end activities, such as accruals and journal entries. The common and reconciled data source facilitates faster and more efficient closing processes.
-
Transparency: The New G/L enhances transparency for auditing and corporate governance in SAP FI, providing greater visibility and control over financial data.
Accounts Payable (SAP FI-AP)
SAP Accounts Payable (FI-AP) is a crucial sub-module that records and administers accounting data for vendors. It integrates with the purchasing system to automatically make postings in response to operative transactions. Additionally, it supplies the cash management application component with invoice figures to optimize liquidity planning. The postings made in FI-AP are simultaneously recorded in various general ledger (G/L) accounts based on the respective transaction.
Accounts Receivable (SAP FI-AR)

Similar to FI-AP, SAP Accounts Receivable (FI-AR) records and manages accounting data for customers. It is an integral part of sales management and directly records postings in the general ledger (G/L). SAP Accounts Receivable offers tools to monitor open items, such as a dunning program that reminds customers of their payables. It also provides data for effective credit management and optimized liquidity planning.
Asset Accounting (SAP FI-AA)
SAP Asset Accounting (FI-AA) is a subsidiary ledger to the general ledger (G/L) that manages an organization’s fixed assets. It can be used in any country and across various industries. FI-AA is integrated with other application areas, allowing for the transfer of data to and from other SAP components. This includes passing on depreciation and interest directly to the financial (FI) and controlling (CO) components.
Bank Accounting (SAP FI-BL)
SAP Bank Accounting (FI-BL) enables efficient management of bank master data, cash balance, and processing of incoming and outgoing payments. It allows organizations to define country-specific characteristics and specifications for payment procedures, ensuring flexibility and compliance.
Special Purpose Ledgers (SAP FI-SL)
SAP Special Purpose Ledgers (FI-SL) enable the creation of ledgers for reporting purposes within SAP Financials. These ledgers can be maintained as general ledgers (G/Ls) or subsidiary ledgers with various account assignment objects. Account assignments can include SAP dimensions from different applications or customer-defined dimensions. While SAP FI-SL is a useful tool, the introduction of the New G/L has reduced the dependence on FI-SL in some scenarios.
SAP Management Accounting (SAP CO)
SAP Management Accounting, also known as SAP Controlling (CO), works in tandem with SAP FI to provide analysts, managers, and financial accountants with the same basic financial data. SAP CO enables the valuation and recording of financial data, serving as the foundation for cost and revenue-related reporting. Although the basic concepts of SAP CO remain the same, the introduction of S/4HANA has brought new functionalities to Management Accounting.
Key Functions of SAP Management Accounting (SAP CO)
SAP CO encompasses several key functions that are vital for effective financial management within organizations:
-
Investment Management: SAP CO facilitates the management of investments, including budgeting, planning, and tracking of investment projects.
-
Master Data Governance: SAP CO ensures the accuracy and consistency of master data, such as cost centers, profit centers, and cost elements.
-
Revenue and Cost Planning: SAP CO enables organizations to plan and forecast revenues and costs, providing insights into future financial performance.
-
Profit Center Accounting: Profit center accounting allows organizations to analyze and evaluate the profitability of individual business units or segments.
-
Product Costing: SAP CO provides tools for calculating and analyzing product costs, enabling organizations to make informed pricing and production decisions.
-
Profitability Analysis: SAP CO allows organizations to analyze the profitability of different market segments, products, or customers.
-
Cost Center Accounting: Cost center accounting tracks and monitors costs associated with specific cost centers, helping organizations manage and control expenses.
-
Transfer Pricing: SAP CO assists in determining appropriate transfer prices for goods and services transferred between different divisions or business units.
Financial Supply Chain Management
SAP Financial Supply Chain Management (FSCM) offers functions to effectively manage the entire financial supply chain and cash flow cycle. It helps collections teams improve receivables management, analyze the root causes of late payments, and proactively handle customer disputes. FSCM integrates with other SAP components to optimize liquidity planning and streamline financial processes.
Treasury Management
SAP Treasury Management provides treasury and cash managers with insights into financial transactions. It checks and controls hedging transactions, cash pooling, and global cash allocation. With straight-through processing, it ensures efficient banking, corporate treasury, and financial accounting processes.
Importance of SAP FI for Financial Professionals
For financial professionals, understanding SAP Finance is of utmost importance. Learning SAP FI provides a solid foundation for becoming an efficient SAP FI consultant and effectively managing financial operations. To gain practical knowledge, it is essential to engage in hands-on learning through SAP FICO courses or SAP S/4HANA Finance training, depending on your background and interests. By mastering SAP FI and its sub-modules, financial professionals can enhance their expertise, meet industry demands, and contribute to the success of their organizations.
Conclusion
SAP FI is a critical module within SAP ERP Financials that enables organizations to streamline financial processes, comply with international accounting standards, and make informed business decisions. With its sub-modules like New General Ledger, Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, Asset Accounting, Bank Accounting, and Special Ledger, SAP FI offers comprehensive solutions for financial management. Combined with SAP CO, organizations can leverage SAP’s powerful tools for cost control, financial supply chain management, and treasury management. For financial professionals, understanding SAP FI is essential for career growth and success in the field. By continuously updating their knowledge and skills, financial professionals can confidently navigate the ever-evolving world of finance with SAP FI.